


Next: Universality
Up: The Standard Model of
Previous: The Formalism
To establish an (or the) objective of the formalism of the gauge
theories which we are going to develop it seems interesting to present
a phenomenological introduction of the weak interactions preparatory
to the unified electroweak model
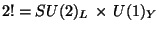 .
.
The weak interactions are the responsible of:
ex2html_comment_mark>54
0)bean
- <
- The continuous spectra of electrons emitted in the
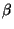 decay of radioactive nuclei.
decay of radioactive nuclei.
- <
- Hadron decays.
- <
- All the reactions induced by neutrinos.
These interactions are characterized by the Fermi coupling constant
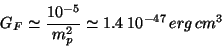 |
(59) |
and by violating the parity symmetry.
To maintain the validity of the energy-momentum conservation law
in the weak processes, induced Pauli to postulate the existence of
the neutrino: neutral particle, of spin 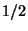 , massless (or
almost) which only interacts weakly.
, massless (or
almost) which only interacts weakly.
The ``basic" reaction, at the hadronic level, is the neutron decay
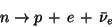 |
(60) |
and for its phenomenological description, Fermi proposed the
interaction Lagrangian
where the first current is associated to the transition of one neutron
in one proton and the second corresponds to the pair
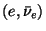 .
All the fields present in the previous currents are written in the same point
corresponding to a point interaction. The Fermi proposal was
certainly inspired by the Lagrangian of electromagnetic interaction.
.
All the fields present in the previous currents are written in the same point
corresponding to a point interaction. The Fermi proposal was
certainly inspired by the Lagrangian of electromagnetic interaction.
![\begin{displaymath}
{\cal L}_{em}= e j_{em}^{\mu}(x) A_{\mu}(x) = e [\bar{\psi}(x) \gamma^{\mu} \psi(x)] [A_{\mu}(x)]
\end{displaymath}](img150.gif) |
(63) |
Later, experimental evidence of other weak reactions different
from neutron decay (62) was found. Besides Dirac's theory indicates that other types
of coupling are also possible. The generalization of the Fermi
Lagrangian (64) is
![\begin{displaymath}
{\cal L} = G_{F} \sum_{i} \alpha_{i} [\bar{\psi}_{p}(x) \...
...si_{n}(x)] [\bar{\psi}_{e}(x) \Gamma_{i} \psi_{\nu_{e}}(x)]
\end{displaymath}](img151.gif) |
(64) |
with the 16 independent matrices 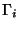 constructed with Dirac's
matrices
constructed with Dirac's
matrices  and the identity. The election of a given
and the identity. The election of a given 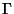 gives place to
a precise transformation law of the corresponding current. For example:
gives place to
a precise transformation law of the corresponding current. For example:
Subsections



Next: Universality
Up: The Standard Model of
Previous: The Formalism
root
2001-01-22
![]() .
.
![]() , massless (or
almost) which only interacts weakly.
, massless (or
almost) which only interacts weakly.